|
|
ADS-2322 Digital Storage Oscilloscope
ADS-2322 Digital Storage Oscilloscope
|
|
The ADS-2322 300MHz bandwidth 2 channel digital storage oscilloscope with a 2.5 GSa/s sample rate and an 8″ color TFT-LCD display with 800x600 resolution offers huge amounts of memory, and USB flash storage support. The unit contains 2 passive probes that are switchable between 1:1 and 10:1 input ratio, and 1 pair of ultimeter leads. Power Supply 110-220V.
Manuals:
|
|
AKTAKOM ADS-2322 digital storage oscilloscope is very slim and lightweight. It has a large screen and a convenient carrying handle. Try and fall in love with it! This digital oscilloscope will always give you a hint how to use it. Just press "HELP" and get User Manual on your oscilloscope's screen! It is ideal for learning and if you forgot any oscilloscope's function.
Features
- 300MHz with 2+1 (External) channels
- 2.5GSa/s
- 10M memory depth for each channel
- Large 8″ 800×600 Pixels LCD display
- AutoScale function
- Pass/Fail function
- Smart design with easy workplace
- Interface: USB Host, USB Device, LAN, VGA
- Nominal entrance: 110-220V 50-60Hz, CATII
Specifications
|
Characteristics
|
Value
|
|
Bandwidth
|
300MHz
|
|
Channel
|
2+1 (External)
|
|
Acquisition
|
Mode
|
Normal, Peak detect, Average
|
|
Sample rate (real time)
|
2.5GSa/s (1.25GSa/s for dual channels)
|
|
Input
|
Input coupling
|
DC, AC, Ground
|
|
Input impedance
|
1MΩ±2%, in parallel with 10pF±5pF
|
|
Probe attenuation factor
|
1X, 10X, 100X, 1000X
|
|
Max. input voltage
|
400V (PK-PK) (DC+AC PK-PK)
|
|
Bandwidth limit
|
20MHz, full bandwidth
|
|
Channel isolation
|
50Hz: 100:1
10MHz: 40:1
|
|
Time delay between channel(typical)
|
150ps
|
|
Horizontal System
|
Sampling rate range
|
0.5Sa/s~2.5GSa/s (single channel), 0.5Sa/s~1.25GSa/s (dual channel)
|
|
Interpolation:
|
Sin(x)/x
|
|
Max Record length
|
Single: 10M (≤1GSa/s), 10K (2GSa/s, 2.5GSa/s)
Dual: 10M (≤500MSa/s), 10K (1GSa/s, 1.25GSa/s)
|
|
Scanning speed (s/div)
|
1ns/div~100s/div, step by 1~2~5
|
|
|
|
Sampling rate / relay time accuracy
|
±100ppm
|
|
Interval (ΔT) accuracy (DC~100MHz)
|
Single: ±(1 interval time + 100ppm × reading + 0.6ns);
Average>16: ±(1 interval time + 100ppm × reading + 0.4ns)
|
|
Vertical system
|
A/D converter
|
8 bits resolution (2 Channels simultaneously)
|
|
Sensitivity
|
2mV/div~10V/div
|
|
Displacement
|
±100V(2V~10V)
|
|
Analog bandwidth
|
60MHz, 100MHz, 200MHz, 300MHz
|
|
Single bandwidth
|
Full bandwidth
|
|
Low Frequency
|
≥5Hz (at input, AC coupling, -3dB)
|
|
Rise time (60MHz)
|
≤1.17ns (at input, Typical)
|
|
DC accuracy
|
±3%
|
|
DC accuracy (average)
|
Average>16: ±(3%rdg+0.05div) for ΔV
|
|
Measurement
|
Cursor
|
ΔV and ΔT between cursors
|
|
Automatic measurement
|
Vpp, Vmax, Vmin, Vamp, Vtop, Vbase, Vavg, Vrms, Overshoot, Preshoot, Freq, Period, Rise time, Fall time, Delay A→B, DelayA→B¯, +Wid, -Wid, +Duty, -Duty
|
|
Waveform Math
|
(+),( -), (*), (/), FFT
|
|
Waveform storage
|
15 waveforms
|
|
Lissajous figure
|
Bandwidth
|
Full bandwidth
|
|
Phase difference
|
±3 degrees
|
|
Frequency (typical)
|
1kHz square wave
|
|
Communication port
|
USB2.0, USB for file storage (file formats *.bmp and *.bin); LAN port
|
Single channel is when only one input channel is working.
Trigger
|
Characteristics
|
Value
|
|
Trigger level range
|
Internal
|
±6div from the screen center
|
|
EXT
|
±600mV
|
|
EXT/5
|
±3V
|
|
Trigger level Accuracy (typical)
|
Internal
|
±0.3div
|
|
EXT
|
±(40mV +6% of Set Value)
|
|
EXT/5
|
±(200mV +6% of Set Value)
|
|
Trigger displacement
|
According to Record length and time base
|
|
Trigger Hold off range
|
100ns~10s
|
|
50% level setting (typical)
|
Input signal frequency ≥50Hz
|
|
Edge trigger
|
slope
|
Rising, Falling
|
|
Sensitivity
|
0.3div
|
|
Pulse trigger
|
Trigger condition
|
Positive pulse: >, <, =
negative pulse: >, <, =
|
|
Pulse Width range
|
30ns~10s
|
|
Video Trigger
|
Modulation
|
Support standard NTSC, PAL and SECAM broadcast systems
|
|
Line number range
|
1-525 (NTSC) and 1-625 (PAL/SECAM)
|
|
Slope Trigger
|
Trigger condition
|
Positive pulse: >, <, =
negative pulse: >, <, =
|
|
Time setting
|
24ns~10s
|
|
Trigger sources
|
Trigger on CH1
|
Edge, Pulse, Video, Slope
|
|
Trigger on CH2
|
Edge, Pulse, Video, Slope
|
General Technical Specifications
Display
|
Display Type
|
8” Colored LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
|
|
Display Resolution
|
800 (Horizontal) × 600 (Vertical) Pixels
|
|
Display Colors
|
65536 colors, TFT screen
|
Output of the Probe Compensator
|
Output Voltage (Typical)
|
About 5V, with the Peak-to-Peak voltage equal to or greater than 1MΩ of load.
|
|
Frequency (Typical)
|
Square wave of 1kHz
|
Power
|
Mains Voltage
|
100~240VAC RMS, 50/60Hz, CAT II
|
|
Power Consumption
|
<24W
|
|
Fuse
|
2A, T grade, 250V
|
|
Battery (optional)
|
Cell: 558792 4000mAh/3.7V
Pack: 2s2p 7.4V/8000mAh
|
Environment
|
Temperature
|
Working temperature: 0°C~ 40°C
Storage temperature: -20°C~ +60°C
|
|
Relative Humidity
|
≤90%
|
|
Height
|
Operating: 3,000m
Non-operating: 15,000m
|
|
Cooling Method
|
Natural convection
|
Mechanical Specifications
|
Dimension
|
340×155×70mm (L*H*W)
|
|
Weight
|
About 1.82kg
|
Accessories
 



| ADS-2322 Digital Storage Oscilloscope - left view |
|
|
| ADS-2322 Digital Storage Oscilloscope - right view |
|
|
| ADS-2322 Digital Storage Oscilloscope - rear view |
|
|
|
| ADS-2322 Digital Storage Oscilloscope - top view |
|
|
| ADS-2322 Digital Storage Oscilloscope - connected to a TV |
|
|
| ADS-2322 Digital Storage Oscilloscope - VGA out |
|
|
|
Analyze the Details of a Signal
Observe the Signal Containing Noises
If the signal is interfered by the noise, the noise may cause a failure in the circuit. For the analyzing of the noise in detail, please operate the instrument according to the following steps:
- Press the Acquire button to display the Acquire menu.
- Press the H1 button to display ACQU Mode menu.
- Press the F2 button to choose Peak detect.
In this case, the screen display contains the waveform of a random noise. Especially when the time base is set as Low Speed, then noise peak and burr contained in the signal can be observed with the peak detection.

Separate Noises from the Signal
When analyze the waveform of a signal, you should remove the noise in it. For the reduction of the random noise in the oscilloscope display, please operate the instrument according to the following steps:
- Press the Acquire button to display the Acquire menu.
- Press the H1 button to display ACQU Mode menu.
- Press the F3 button, turn the M knob and observe the waveform obtained from averaging the waveforms of different average number.
After the averaging, the random noise is reduced and the detail of the signal is easier to be observed. Shown as follows, after the noise is removed, the burrs on the rising and falling edges appear.

Application of X-Y Function
Examine the Phase Difference between Signals of two Channels
Example: Test the phase change of the signal after it passes through a circuit network.
Connect the oscilloscope with the circuit and monitor the input and output signals of the circuit.
For the examination of the input and output of the circuit in the form of X-Y coordinate graph, please operate according to the following steps:
- Set the probe menu attenuation coefficient for 10X and that of the switch in the probe for 10X.
- Connect the probe of channel 1 to the input of the network and that of Channel 2 to the output of the network.
- Push down the Autoset button, with the oscilloscope turning on the signals of the two channels and displaying them in the screen.
- Turn the VOLTS/DIV knob, making the amplitudes of two signals equal in the rough.
- Press the Display button and recall the Display menu.
- Press the H3 button and choose XY Mode as ON.
The oscilloscope will display the input and terminal characteristics of the network in the Lissajous graph form.
- Turn the VOLTS/DIV and VERTICAL POSITION knobs, optimizing the waveform.
- With the elliptical oscillogram method adopted, observe and calculate the phase difference.
Based on the expression sin q=A/B or C/D, there into, q is the phase difference angle, and the definitions of A, B, C, and D are shown as the graph above. As a result, the phase difference angle can be obtained, namely, q =± arcsin (A/B) or ± arcsin (C/D). If the principal axis of the ellipse is in the I and III quadrants, the determined phase difference angel should be in the I and IV quadrants, that is, in the range of (0~π/2) or (3π/2~2π). If the principal axis of the ellipse is in the II and IV quadrants, the determined phase difference angle is in the II and III quadrants, that is, within the range of (π/2~π) or (π~3π/2).

Capture the Single Signal
The digital storage oscilloscope takes the lead in providing the convenience capturing of such non-periodic signals as pulse and burr, etc. If you intent to capture a single signal, you cannot set the trigger level and the trigger edge unless you have particular prior knowledge of this signal. For example, if the pulse is the logic signal of a TTL level, the trigger level should be set to 2 volts and the trigger edge be set as the rising edge trigger. If it is uncertain as to the signal, you can make an observation of it in advance under the automatic or ordinary mode to determine the trigger level and the trigger edge.
The operation steps are as follows:
- Set the probe menu attenuation coefficient to 10X and that of the switch in the probe to 10X
- Adjust the VOLTS/DIV and SEC/DIV knobs to set up a proper vertical and horizontal ranges for the signal to be observed.
- Press the Acquire button to display the Acquire menu.
- Press the H1 button to display the Acquire Mode menu.
- Press the F2 button to choose Peak detect.
- Press the Trigger Menu button to display the Trigger menu.
- Press the H1 button to display the Trigger Type menu.
- Press the F1 to choose Single as the type.
- Turn the M knob to choose Edge as the mode.
- Press the H2 button to display the Source menu.
- Press the F1 button to choose CH1 as the source.
- Press the H3 button to display the Coupling menu; press the F2 button to choose DC as the Coupling.
- Press the H4 button to choose (rising) as the Slope.
- Rotate the TRIG LEVEL knob and adjust the trigger level to the mid-value of the signal to be measured.
- If the Trigger State Indicator at the top of the screen does not indicate Ready, push down the Run/Stop button and start acquiring, waiting the emergence of the signal in conformity with the trigger conditions. If a signal reaches to the set trigger level, one sampling will be made and then displayed in the screen. With this function, any random occurrence can be captured easily. Taking the burst burr of larger amplitude for example, set the trigger level to the value just greater than the normal signal level, and then presses the Run/Stop button and waits. When there is a burr occurring, the instrument will trigger automatically and record the waveform generated during the period around the trigger time. With the HORIZONTAL POSITION knob in the horizontal control area in the panel rotated, you can change the horizontal position of the trigger position to obtain the negative delay, making an easy observation of the waveform before the burr occurs.

Measurement of Simple Signals
Observe an unknown signal in the circuit, and display and measure rapidly the frequency and peak-to-peak voltage of the signal.
1. Carry out the following operation steps for the rapid display of this signal:
- Set the probe menu attenuation coefficient as 10X and that of the switch in the probe switch as 10X
- Connect the probe of Channel 1 to the measured point of the circuit.
- Push down the Autoset button.
The oscilloscope will implement the Autoset to make the waveform optimized, based on which, you can further regulate the vertical and horizontal divisions till the waveform meets your requirement.
2. Perform Automatic Measurement
The oscilloscope can measure most of the displayed signals automatically. To measure the period and frequency of the Channel 1 and the mean and peak-to-peak voltage of the Channel 2, follow below steps:
- Press the Measure button to show the automatic measurement function menu.
- Press the H1 to display the Add menu.
- Press the F2 button to choose CH1 as the source.
- Press the F1 button, the type items will display at the left of screen, and turn the M knob to choose Period.
- Press the F4 button, the period measurement will be added.
- Press the F1 button again, the type items will display at the left of screen, and turn the M knob to choose Freq.
- Press the F4 button, the frequency measurement will be added, finish settings of channel 1.
- Press the F2 button to choose CH2 as the source.
- Press the F1 button, the type items will display at the left of screen, and turn the M knob to choose Mean.
- Press the F4 button, the mean measurement will be added.
- Press the F1 button, the type items will display at the left of screen, and turn the M knob to choose PK-PK.
- Press the F4 button, the peak-to-peak voltage measurement will be added, finish settings of channel 2.
Then, the period, frequency, mean and peak-to-peak voltage will be displayed at the bottom left of the screen and change periodically

Measuring Gain of the Amplifier in the Metering Circuit
Set the probe menu attenuation coefficient as 10X and that of the switch in the probe as 10X.
Connect the oscilloscope CH1 channel with the circuit signal input end and the CH2 channel to the output end.
Operation Steps:
- Push down the Autoset button and the oscilloscope will automatically adjust the waveforms of the two channels into the proper display state.
- Push down the Measure button to show the Measure menu.
- Press the H1 button.
- Press the F2 button and choose CH1.
- Press the F1 button and turn the M knob to choose PK-PK.
- Press the F2 button and choose CH2.
- Press the F1 button again and turn the M knob to choose PK-PK
- Read the peak-to-peak voltages of Channel 1 and Channel 2 from the bottom left of the screen
- Calculate the amplifier gain with the following formulas.
Gain = Output Signal / Input signal
Gain (db) = 20•log (gain)

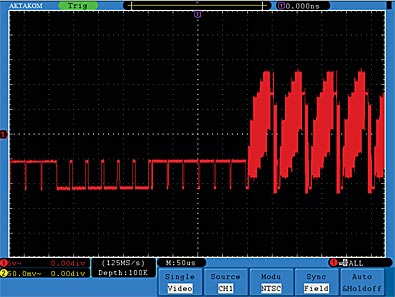
Video Signal Trigger
Observe the video circuit of a television, apply the video trigger and obtain the stable video output signal display.
Video Field Trigger
For the trigger in the video field, carry out operations according to the following steps:
- Press the Trigger Menu button to display the trigger menu.
- Press the H1 button to display the trigger type menu.
- Press the F1 button to choose Single for Type.
- Turn the M knob to choose Video as the mode.
- Press the H2 button to display the Source menu.
- Press the F1 button to choose CH1 for Source.
- Press the H3 button to display the Module menu.
- Press the F1 button to choose NTSC for the modulation.
- Press the H4 button to display the sync menu.
- Press the F2 button to choose Field for Sync.
- Turn the VOLTS/DIV, VERTICAL POSITION and SEC/DIV knobs to obtain a proper waveform display.
Frequently Asked Questions
After the Average value sampling is set in the Acqu Mode or the longer duration is set in the Persist in Display the display rate is slowed down
How can oscillogram data be saved for further reading in MS Excel?
Connecting to your device through LAN
Frozen screen or memory full
How to change language settings
How to see my Serial Number?
No Display Responses to the Push-down of RUN/STOP
The measured voltage amplitude value is 10 times greater or smaller than the actual value
How to save data in a USB Flash Drive?
After the oscilloscope is powered on the display remains dark, what should I do?
The signal is displayed as ladder like waveform
There is wave form displayed, but it is not stable
When changing the horizontal sweep on the digital oscilloscope at different horizontal points observed inexplicable change in the form of the same signal, why is this happening?
| After the Average value sampling is set in the Acqu Mode or the longer duration is set in the Persist in Display the display rate is slowed down |
It is a normal phenomenon.
Up
|
| How can oscillogram data be saved for further reading in MS Excel? |
Normally the oscilloscope allows saving files to flash memory in *.bmp and *.bin formats. To save oscillogram data for further reading in MS Excel you may use Aktakom DSO-Reader Light or Aktakom DSO-Reader Pro software which saves oscillogram data in AUL format. Saved in AUL format files can be converted (using Aktakom AULFConverter program) into *.csv format that can be read in MS Excel program. For more information refer to Aktakom AULFConverter description.
Up
|
| Connecting to your device through LAN |
|
Using your DS-WAVE application software you may connect to your device through LAN. Please follow the example below

then you will be able to type the IP you configured in your device. The factory default IP is 192.168.1.72 but if your LAN range is on a different octave please change the IP and GW in your equipment to the correct mask. The application port is 3000 please don't change it

Up
|
| Frozen screen or memory full |
|
During long period of extreme oscilloscope operations with dual channel different signals the use of memory may freeze the equipment instead of switch it off so you may hold last measurement.
Frozen screen in those cases is not a general malfunction instead you do make it run out of memory.

Extreme use of memory is not supported for more than 5 to 10 minutes of permanent measurements
Up
|
| How to change language settings |
|
Step 1. Turn ON Oscilloscope
Step 2. Press UTILITY button

Step 3. Press H2 button

Step 4. Scroll language options using main control knob


Step 5. Press H1 button Configure

Up
|
| How to see my Serial Number? |
|
Your serial number is printed in a label with barcode in a back of your oscilloscope as well as in a box but if you want to confirm that number you may press the utility button and go to config (H1) and press about (H5)

Your serial number will be display in your screen

Up
|
| No Display Responses to the Push-down of RUN/STOP |
|
Check whether Normal or Signal is chosen for Polarity in the TRIG MODE menu and the trigger level exceeds the wave form range. If it is, make the trigger level is centered in the screen or set the trigger mode as Auto. In addition, with the AUTOSET button pressed, the setting above can be completed automatically.
Up
|
| The measured voltage amplitude value is 10 times greater or smaller than the actual value |
Check whether the channel attenuation coefficient and the attenuation coefficient of the probe used is match.
Up
|
| How to save data in a USB Flash Drive? |
|
This oscilloscope allows you to save data to an external USB Flash Drive only if the drive is formatted with FAT32.

If you haven't noticed one huge change with Windows 7 is that FAT32 is no longer an option on formatting drives. You are now left with the options of either NTFS or exFAT. OK so your asking what is exFAT? Well its not FAT32, acutally its compatible with FAT64.

So let's Format external USB Flash drive with FAT32 using DOS
First you need to find what your Hard Drive is named (the label) that is easy to do right click on the hard drive and it will show you in the top box. As you can see mine has no level in the picture bellow. You also need to note which drive letter it is. Mine is Drive: G.
Next thing you need to do is to find your command prompt

Once you get to command prompt you will need to type this:
format /FS:FAT32 G:
Note: You need to change the letter G to the letter of your drive

Then just answer the questions as you like for a volume label, etc. It will take time according to the driver size.

Now for more information of "How to Save and Recall a Waveform details" go to equipment User's Guide or find it by the following links:
- For the ADS-2061M go to PDF page 53 (49 if printed) and do not forget that a USB Flash Drive is an external memory. See User's Guide.
- For all other ADS models (2022, 2042M, 2061M, 2062 & M, 2102 & M, 2152 & M) go to PDF page 42 (74 if printed) See User's Guide.
Up
|
| After the oscilloscope is powered on the display remains dark, what should I do? |
|
Please implement the following fault treatment procedure.
- Check whether the power cable is connected properly.
- Ensure the power switch is turned on.
- Restart the instrument after completing the checks above.
- If the oscilloscope still can not work normally, please call for service.
Up
|
| The signal is displayed as ladder like waveform |
- The time base setting maybe is too slow. Turn the horizontal SCALE knob to increase horizontal resolution.
- Maybe the display Type is set to "Vectors". Set it to "Dots" mode.
Up
|
| There is wave form displayed, but it is not stable |
- Check whether the Source item in the TRIG MODE menu is in conformity with the signal channel used in the practical application.
- Check on the trigger Type item: The common signal chooses the Edge trigger mode for Type and the video signal the Video. Only if a proper trigger mode is applied, the wave form can be displayed steadily.
- Try to change the trigger coupling into the high frequency suppress and the low frequency suppress to smooth the high frequency or low frequency noise triggered by the interference.
Up
|
| When changing the horizontal sweep on the digital oscilloscope at different horizontal points observed inexplicable change in the form of the same signal, why is this happening? |
|
In fact, this is not a problem.
Just keep in mind that you're using a digital oscilloscope, which digitizes the signal with different sampling rates depending on the selected horizontal sweep, and then connects the digitized points with strait line while restoring the real shape of the signal.
Your first screen shows that you are measuring voltage 50 Hz with the 10 ms / div sweep and a sampling frequency of 20 kHz Ks/s
One signal period (20 ms), digitized in this mode, 20E-03 (sec) * 20E03 (1/sec) = 400 points. This is enough to properly restore and interpolate a sine wave of 50 Hz (i.e. in a period of 20 ms).
Normal display, with a sweep 10 ms / div:
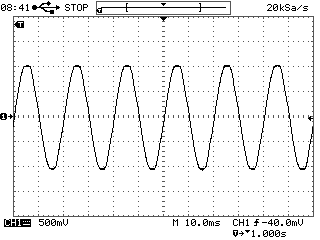
Distortion of the same signal at 10 s / div sweep
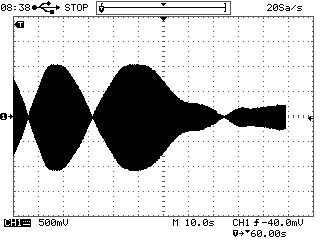
Your second screen is set to sweep 10 sec / div, and sample rate on a sweep turned to 20 samples per second (20 Sa / s). I.e. one signal period 20 ms had: 20E-03 (sec) * 20 (1/sec) = 0.4 points. That means that to restore (to interpolate the points) a sine wave with less than one point in time is impossible, so you get this mess (known as "aliasing" or a false frequency) formed by the beats of the measured frequency and sampling frequency.
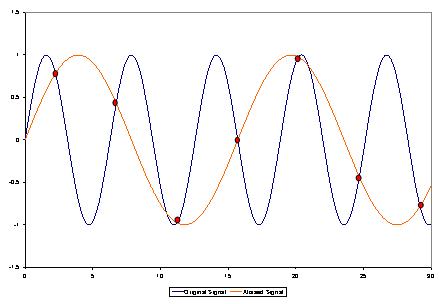
In order to correctly install a data collection in a digital oscilloscope one should follow a simple rule - the sampling rate must be at least 5-10 times higher than the frequency signal, in that case you will not have the issues that we just discussed.
This applies to all digital oscilloscopes and in no way connected to any particular make or model of oscilloscope or its probes.
Up
|
Back to the section
|
|